
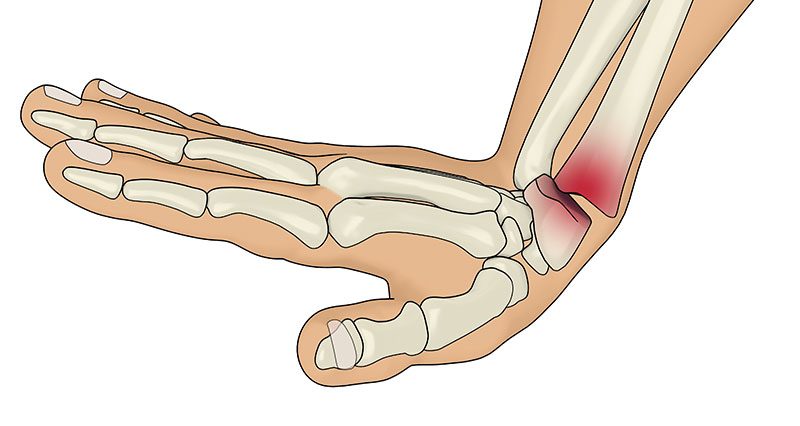
"Adult distal radius fractures classification systems: essential clinical knowledge or abstract memory testing?". ^ Shehovych A, Salar O, Meyer C, Ford DJ (November 2016)."Smith's fracture generally occurs after falling on the palm of the hand".
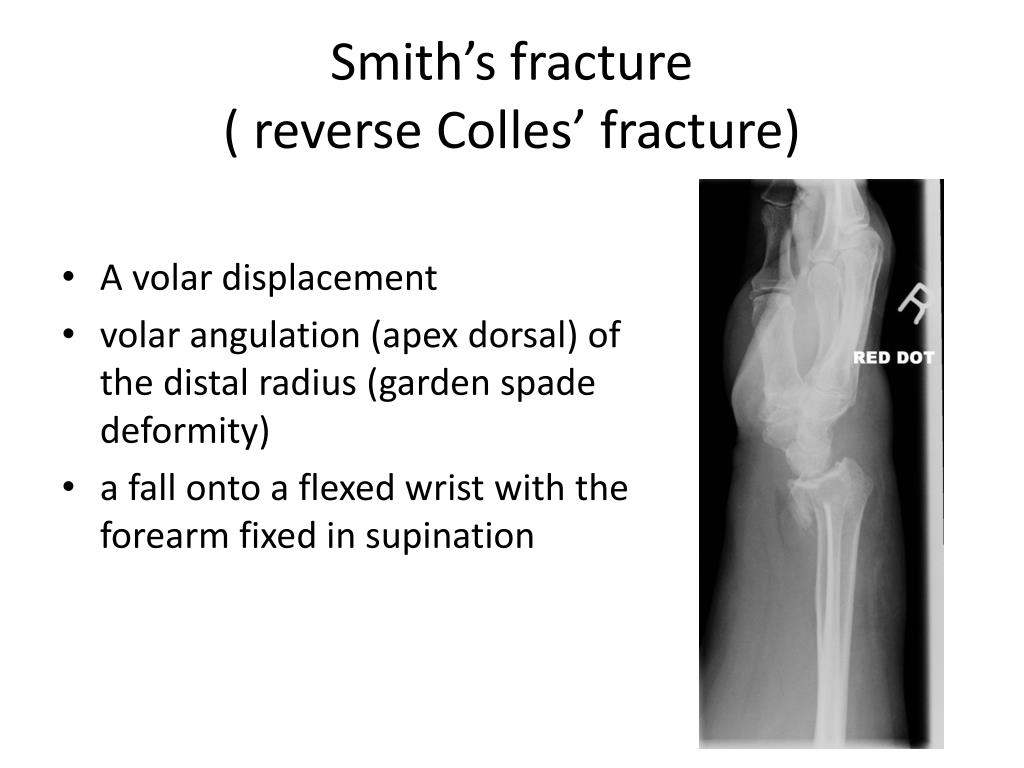
^ Stead LG, Stead SM, Kaufman MS (2006).Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary (18th ed.). This fracture is named after the orthopedic surgeon, Robert William Smith (1807–1873) in his book A Treatise on Fractures in the Vicinity of Joints, and on certain forms of Accidents and Congenital Dislocations published in 1847. In the case of a Smith's fracture, the wrist must be reduced and splinted in extension. įor a closed reduction, the approach is the opposite of reductions completed for Colle's fractures. Indications for operative management include dorsal or volar comminution, intra-articular involvement, instability post-reduction, angulation greater than 20 degrees, surface step-off over 2mm or shortening of the radius greater than 5mm. An open fracture will always require surgical intervention. Significant angulation and deformity may require an open reduction and internal fixation. A fracture with mild angulation and displacement may require closed reduction (putting into place without surgery). An undisplaced fracture may be treated with a cast alone. Treatment of this fracture depends on the severity of the fracture. Lateral radiography will demonstrate volar angulation / displacement of the fracture. PA radiography will look very similar to a Colles' fracture, with a fracture along the distal metaphysis of the radius (can be shortened or comminuted). Two views should be obtained: AP and lateral. Diagnosis Physical examination Ĭlassic physical examination findings of a Smith's fracture is palmar displacement of the wrist that results in a "garden-spade deformity". Ĭomplex regional pain syndrome can be reported in up to 40% of fractures. Įntrapment of the extensor pollicis longus can also occur in cases of non-union, and can result in late rupture of this tendon. There are also higher risks of carpal tunnel syndrome and osteoarthritis in patients with a previous Smith fractures.
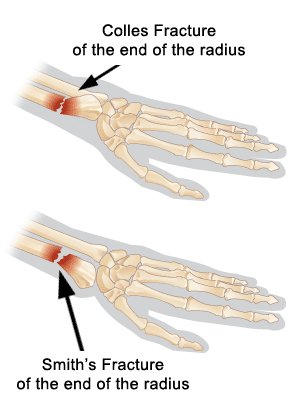
This can result in a permanent "garden-spade deformity". The biggest concern is malunion of the wrist due to poor reduction or shortening of the distal radius.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
